Unveiling Distributed Validator Technology (DVT): Expanding Decentralization Beyond Ethereum
As blockchain networks mature, particularly those utilizing Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms, decentralization remains critical. However, the growth of liquid staking and re-staking protocols has raised concerns about centralization, even in systems designed to avoid it. Distributed Validator Technology (DVT) offers a compelling solution by enhancing resilience, security, and economic efficiency. While DVT has gained traction in Ethereum, its potential goes far beyond, offering a transformative approach to decentralization across other PoS networks.

What is Distributed Validator Technology (DVT)?
At its core, DVT splits the responsibility of a validator across multiple independent nodes, distributing trust and reducing the risks inherent in centralized validation. Each node holds only part of the validator’s private key, secured through splitting the Boneh-Lynn-Shacham (BLS) validator key into multiple key shares using Distributed Key Generation (DKG). This allows signature aggregation without revealing the complete key. This distributed setup creates a more resilient system, as no single node or operator holds full control of the validator’s key.

Key Features of DVT:
- Fault Tolerance: If up to ⅓ of the nodes in a DVT cluster fail, the network continues to function, allowing validators to earn full rewards without interruption.
- Enhanced Security: By distributing key control, it becomes significantly harder for any single entity to compromise the network.
- True Decentralization: Encourages a diverse range of participants by lowering the barrier to becoming a validator, thus preventing centralization by large operators.
Economic Efficiency: A Unique Marketplace for Resource Utilization
One of the often-overlooked benefits of DVT is its potential to create an efficient marketplace for validator resources. In traditional staking models, validators must maintain infrastructure even when it’s underutilized. With DVT, networks can dynamically allocate validator tasks across nodes with available resources, optimizing the system’s overall efficiency.
This approach has several advantages:
- Resource Optimization: Instead of idle infrastructure, validators can tap into a pool of resources as needed, reducing operational costs.
- Dynamic Scalability: Networks can adjust to varying workloads by distributing tasks among a wide array of nodes, ensuring smooth operations even during peak demand.
- Increased Participation: Smaller validators can enter the marketplace, contributing to the network’s security without requiring the full overhead of running standalone infrastructure.
By fostering a flexible and dynamic environment, DVT enables networks to maximize their computational and staking potential, making the entire system more efficient, sustainable, and accessible.

Resilience and Decentralization: Mitigating Centralization Risks
Without DVT, blockchain networks, especially those implementing liquid staking, risk concentrating power in the hands of a few large operators. This centralization not only undermines the ethos of blockchain but also introduces serious security and operational risks, such as:
- Validator Monopolies: A few centralized validators could control most of the staked assets.
- Single Points of Failure: If one of these centralized entities is compromised or experiences downtime, it could affect a significant portion of the network.
- Censorship Vulnerabilities: A concentrated group of validators could collude to censor transactions, undermining the integrity of the blockchain.
DVT solves these issues by distributing validation tasks across a wider group of participants, enhancing the overall decentralization of the network. If some validators fail, the network remains operational, ensuring up to ⅓ of the validators in a DVT cluster can fail without impacting performance. This level of resilience is vital for maintaining user trust and ensuring the network can operate smoothly even under duress.
Beyond Ethereum: The Future of DVT in Other PoS Networks
While DVT has gained traction within Ethereum, particularly through implementations like SSV Network and Obol Collective, its potential extends far beyond. Other PoS networks, such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and Cardano, can benefit significantly from integrating DVT.
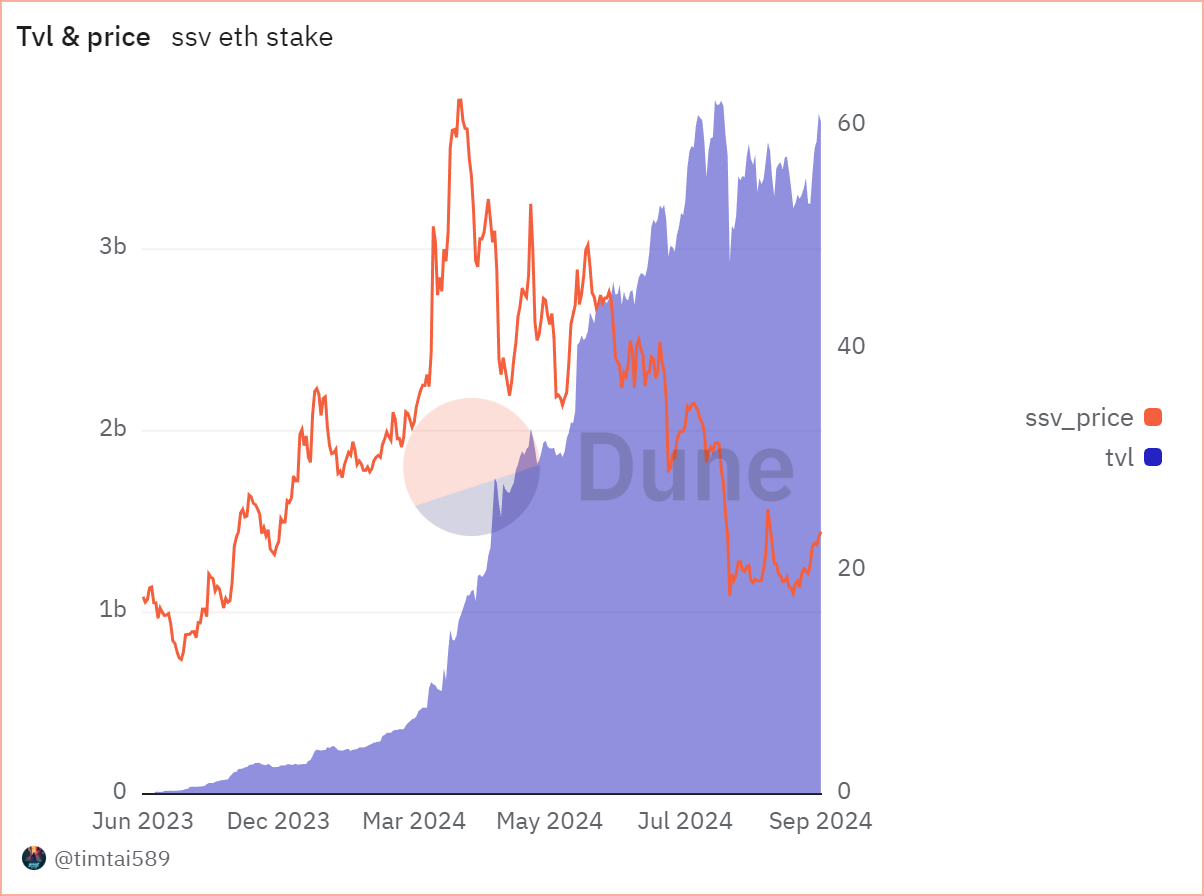
Ethereum TVL on SSV has been steadily increasing since its initial launch.
Expanding to Other Networks:
- Polkadot: With its multi-chain structure, DVT could be used to decentralize validation across different parachains, increasing security and operational flexibility.
- Cosmos: Given its focus on interoperability between blockchains, DVT could enhance the security of cross-chain operations by distributing validator responsibilities across multiple networks.
- Cardano: DVT could strengthen Cardano’s staking model by reducing reliance on large staking pools and encouraging wider participation from smaller validators.
The decentralized nature of DVT makes it adaptable across different PoS ecosystems, ensuring that each network can benefit from increased security, resilience, and decentralization.
Real-World Implementations and the Role of Node.Monster
At Node.Monster, we’re committed to driving forward the adoption of DVT, particularly within the ether.fi validator stack, where we operate validators with high efficiency and performance. Our work in this area isn’t limited to Ethereum. We see the broader application of DVT across multiple PoS networks as critical for the long-term health and decentralization of blockchain systems.
Alongside our work with ether.fi, protocols like Lido are also exploring the benefits of DVT. Lido’s SimpleDVT initiative aims to decentralize its validator set further, ensuring that the concentration of staked ETH does not lead to centralization risks. Similarly, Renzo Protocol is pushing the boundaries of DVT integration, building a decentralized staking system that prioritizes security and robustness.
These projects highlight the growing realization across the industry that DVT is not just an Ethereum solution — it’s a blockchain-wide innovation that ensures the longevity and resilience of decentralized systems.
At Node.Monster, our mission aligns with the core principles of Ethereum — security, decentralization, and innovation.
- Future-Proofing Ethereum: Addressing centralization risks proactively.
- Empowering Users: Allowing more participants to engage in staking without intermediaries.
- Strengthening the Network: Enhancing security and resilience through distributed operations.

